Hi, Here is
Weizhi Tang
A Researcher in Neuro-Symbolic AI; The Founder of nouer.app; A Developer in Frontend, Flutter, Backend, and Cloud; A Songwriter in Pop and R&B.
NEWS
📰Nouer is launched!
Feb, 2026An AI-powered opinionated knowledge system for interdiscipline and life-long learner
LaunchPaper Accepted at ACL Findings 2025
May, 2025HyGenar: An LLM-Driven Hybrid Genetic Algorithm for Few-Shot Grammar Generation
PublicationPaper Accepted at NeSy 2024 as Spotlight
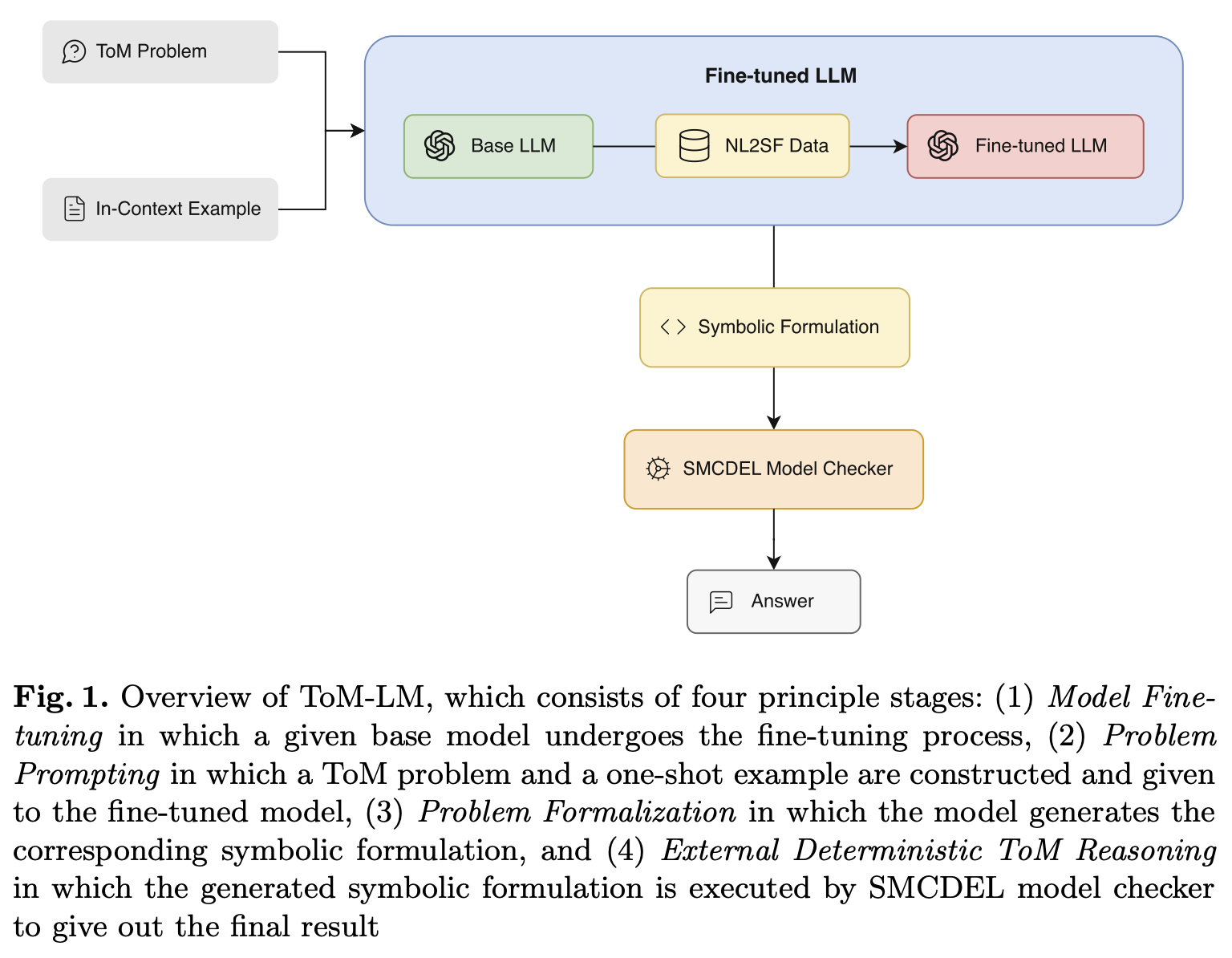
Apr, 2024ToM-LM: Delegating Theory Of Mind Reasoning to External Symbolic Executors in Large Language Models
Publication
EDUCATION
🎓University of Edinburgh
2024 - Present
PhD in Computer Science
National University of Singapore
2021 - 2022
MSc in Data Science and Machine Learning
University of Colorado Boulder
2018 - 2020
BA in Computer Science & Psychology (Distinction)
PAPERS
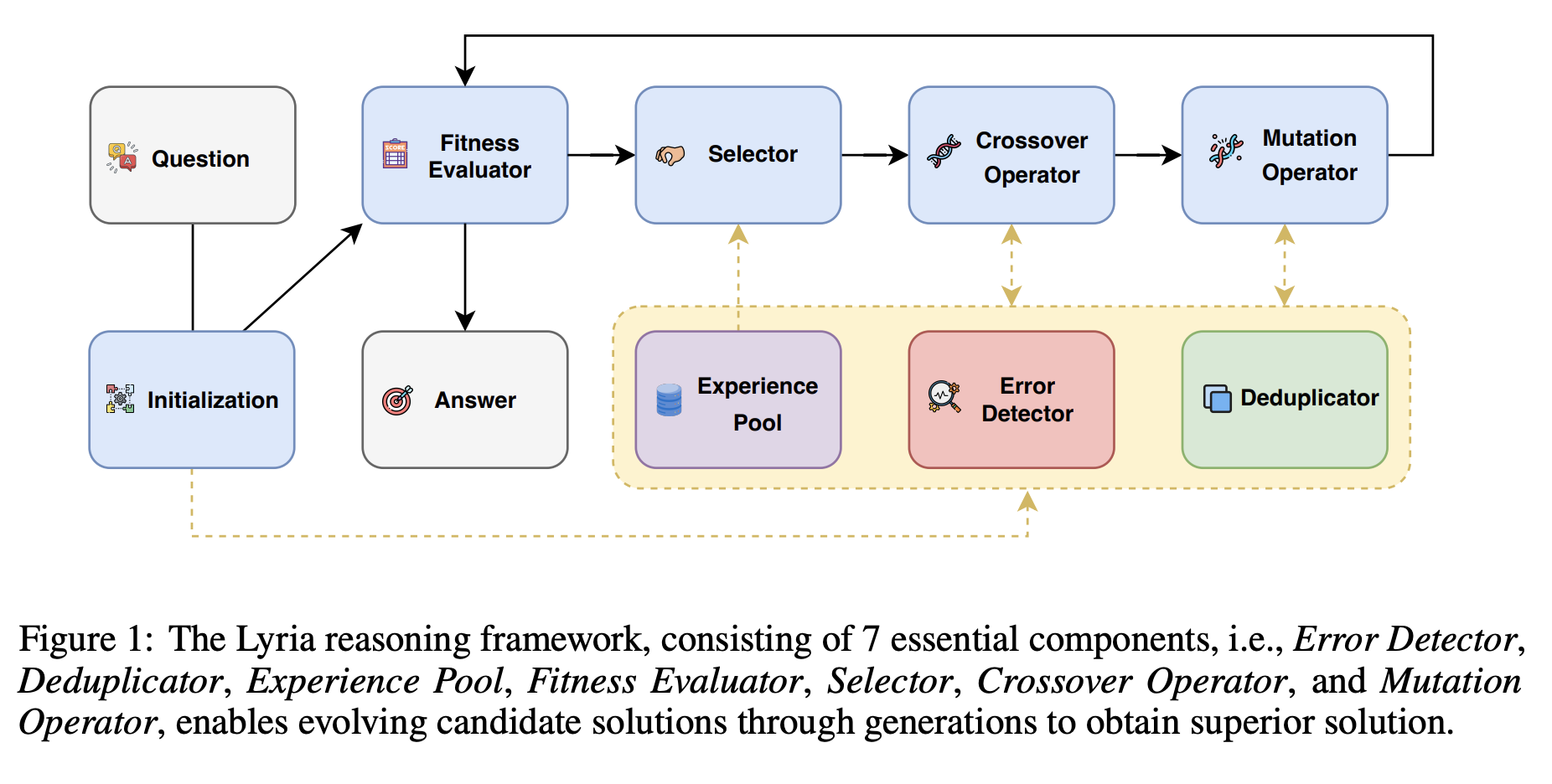
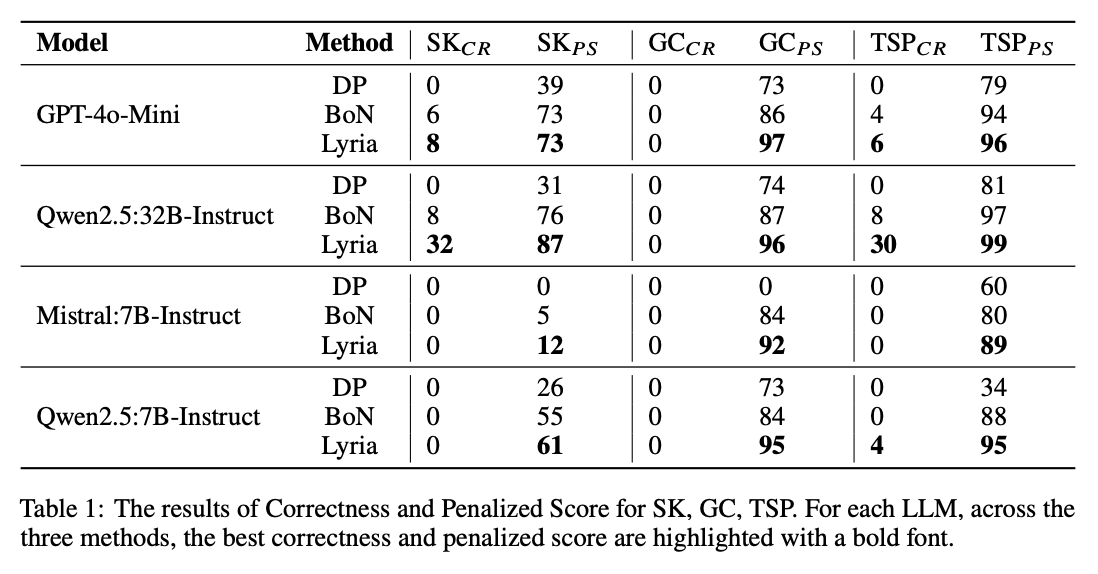
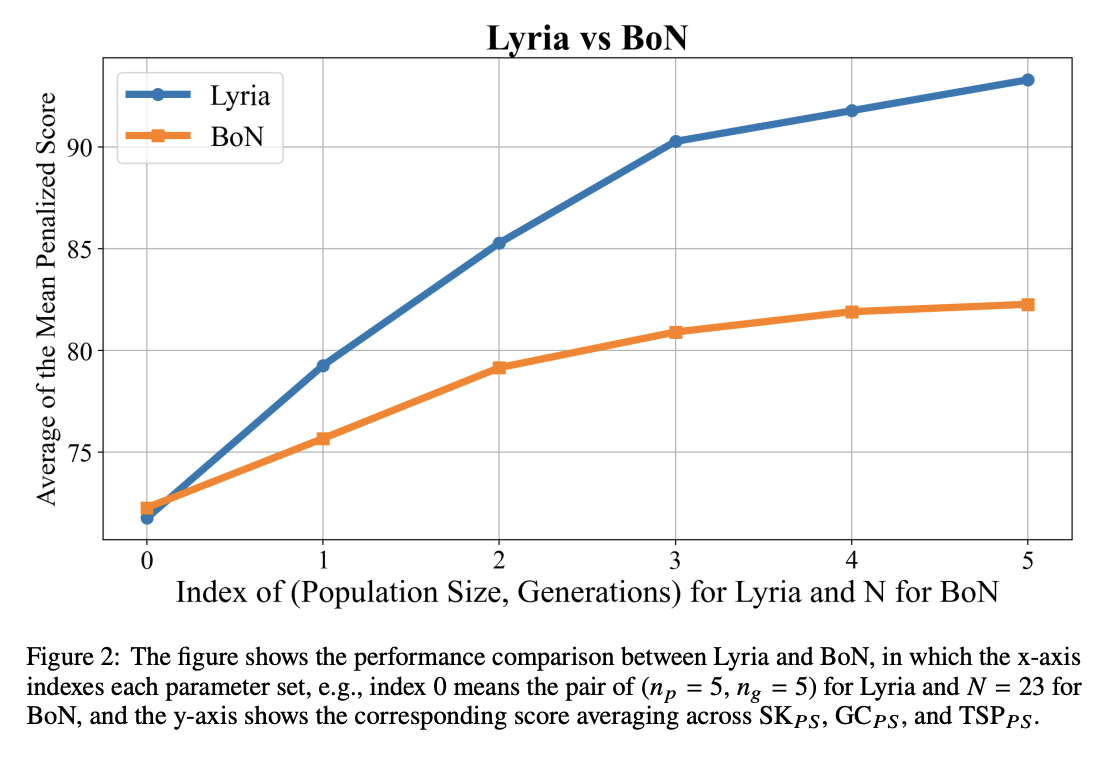
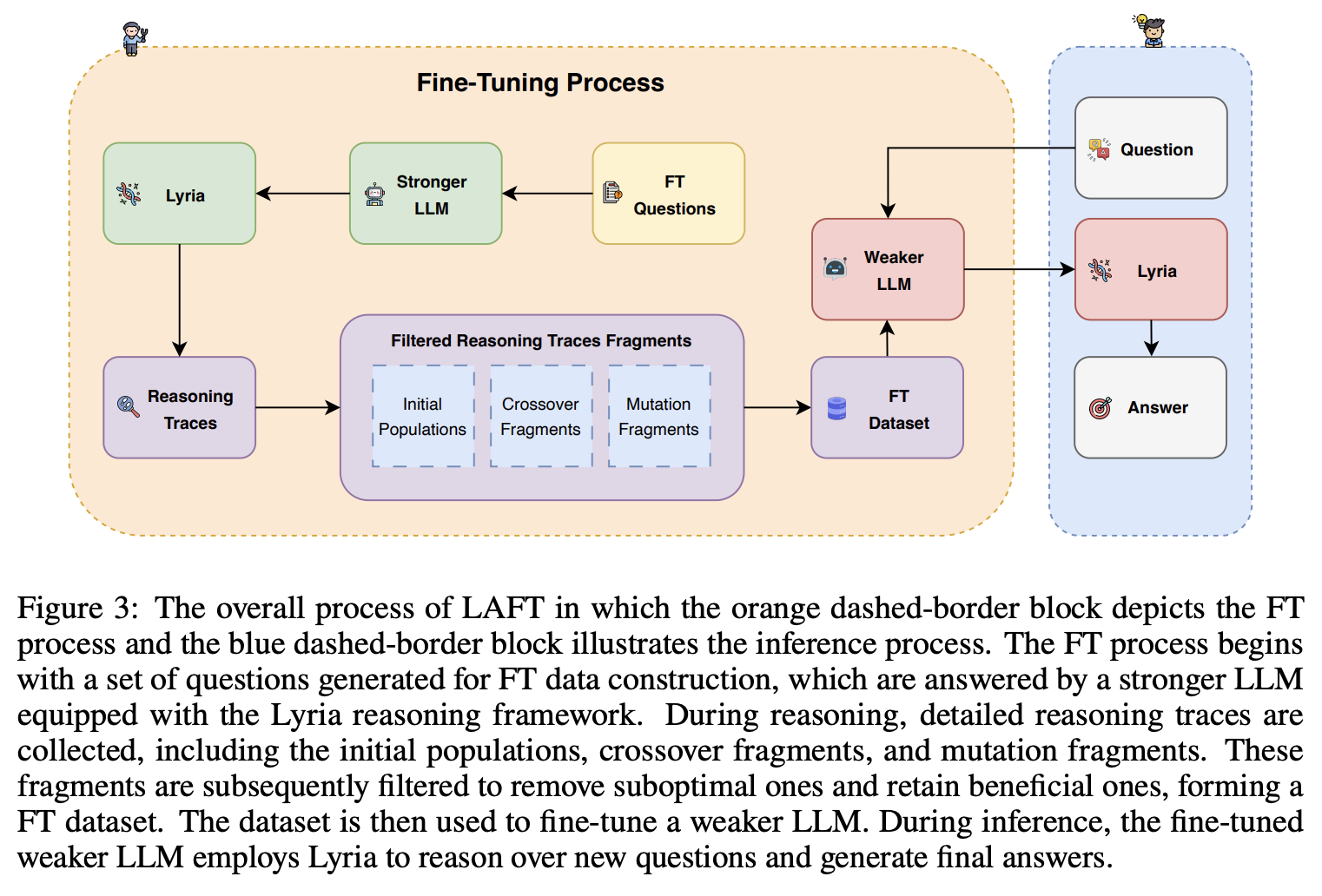
🎓Lyria: A Genetic Algorithm-Driven Neuro-Symbolic Reasoning Framework for LLMs
W Tang, K Nuamah, V Belle
While LLMs have demonstrated impressive abilities across various domains, they struggle with two major issues. The first is that LLMs trap themselves into local optima and the second is that they lack exhaustive coverage of the solution space. To investigate and improve these two issues, we propose Lyria, a neuro-symbolic reasoning framework building on the integration of LLMs, genetic algorithms, and symbolic systems, comprising 7 essential components. Through conducting extensive experiments with 4 LLMs across 3 types of problems, we demonstrated the efficacy of Lyria. Furthermore, with 7 additional ablation experiments, we further systematically analyzed and elucidated the factors that affect its performance. In addition, based on Lyria, we extend the ideas to the fine-tuning process of LLMs and introduce LAFT which enables a weaker model to imitate the reasoning process of a stronger model that reason under the Lyria reasoning framework. We demonstrate that the significant effectiveness of LAFT by conducting extensive experiments against 9 constructed baselines. We finally reveal the limitations and provide insights into future directions.

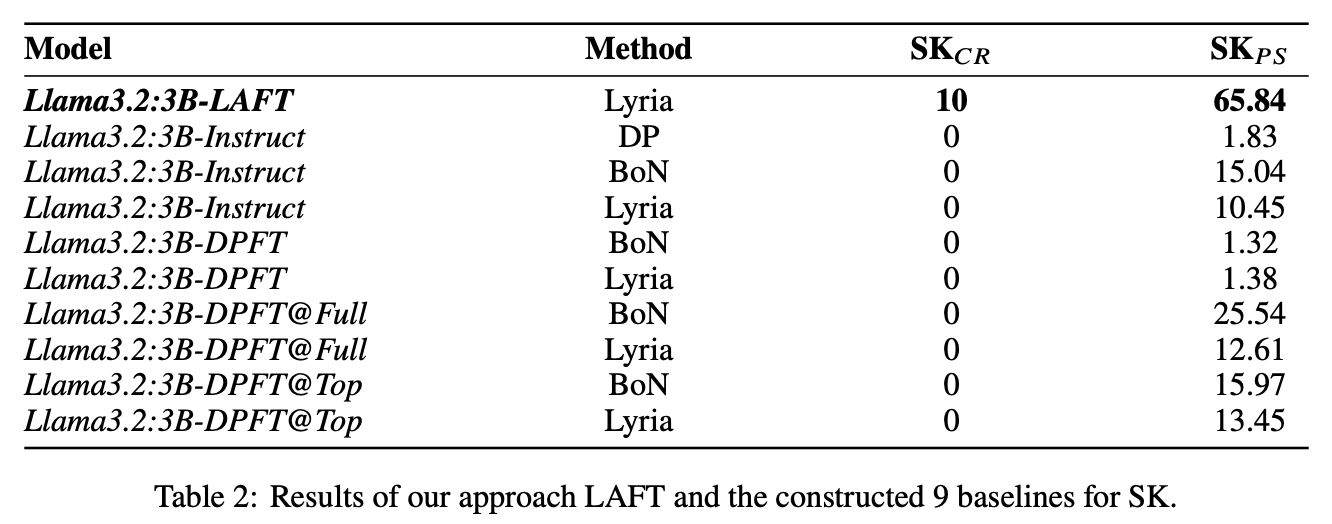
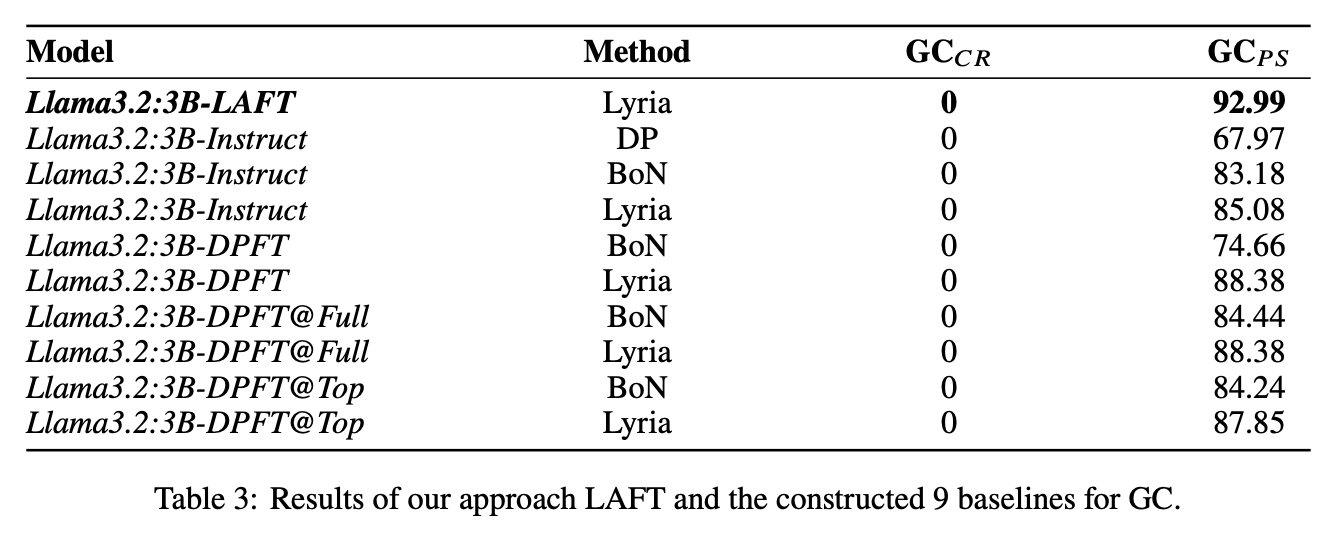
 Preprint Jul 2025
Preprint Jul 2025HyGenar: An LLM-Driven Hybrid Genetic Algorithm for Few-Shot Grammar Generation
W Tang, Y Li, C Sypherd, E Polgreen, V Belle
ACL 2025 Findings
Grammar plays a critical role in natural language processing and text/code generation by enabling the definition of syntax, the creation of parsers, and guiding structured outputs. Although large language models (LLMs) demonstrate impressive capabilities across domains, their ability to infer and generate grammars has not yet been thoroughly explored. In this paper, we aim to study and improve the ability of LLMs for few-shot grammar generation, where grammars are inferred from sets of a small number of positive and negative examples and generated in Backus-Naur Form. To explore this, we introduced a novel dataset comprising 540 structured grammar generation challenges, devised 6 metrics, and evaluated 8 various LLMs against it. Our findings reveal that existing LLMs perform sub-optimally in grammar generation. To address this, we propose an LLM-driven hybrid genetic algorithm, namely HyGenar, to optimize grammar generation. HyGenar achieves substantial improvements in both the syntactic and semantic correctness of generated grammars across LLMs.
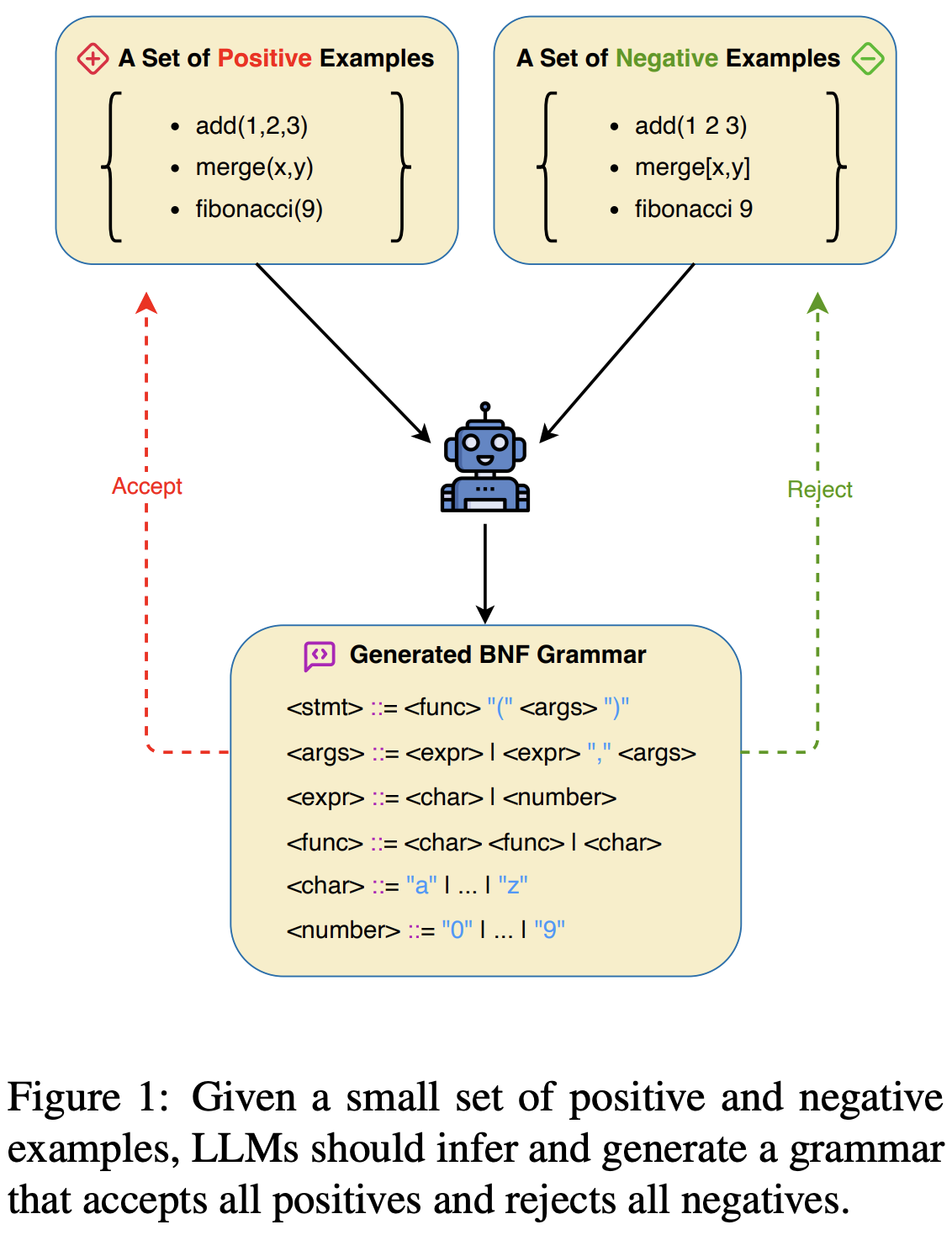
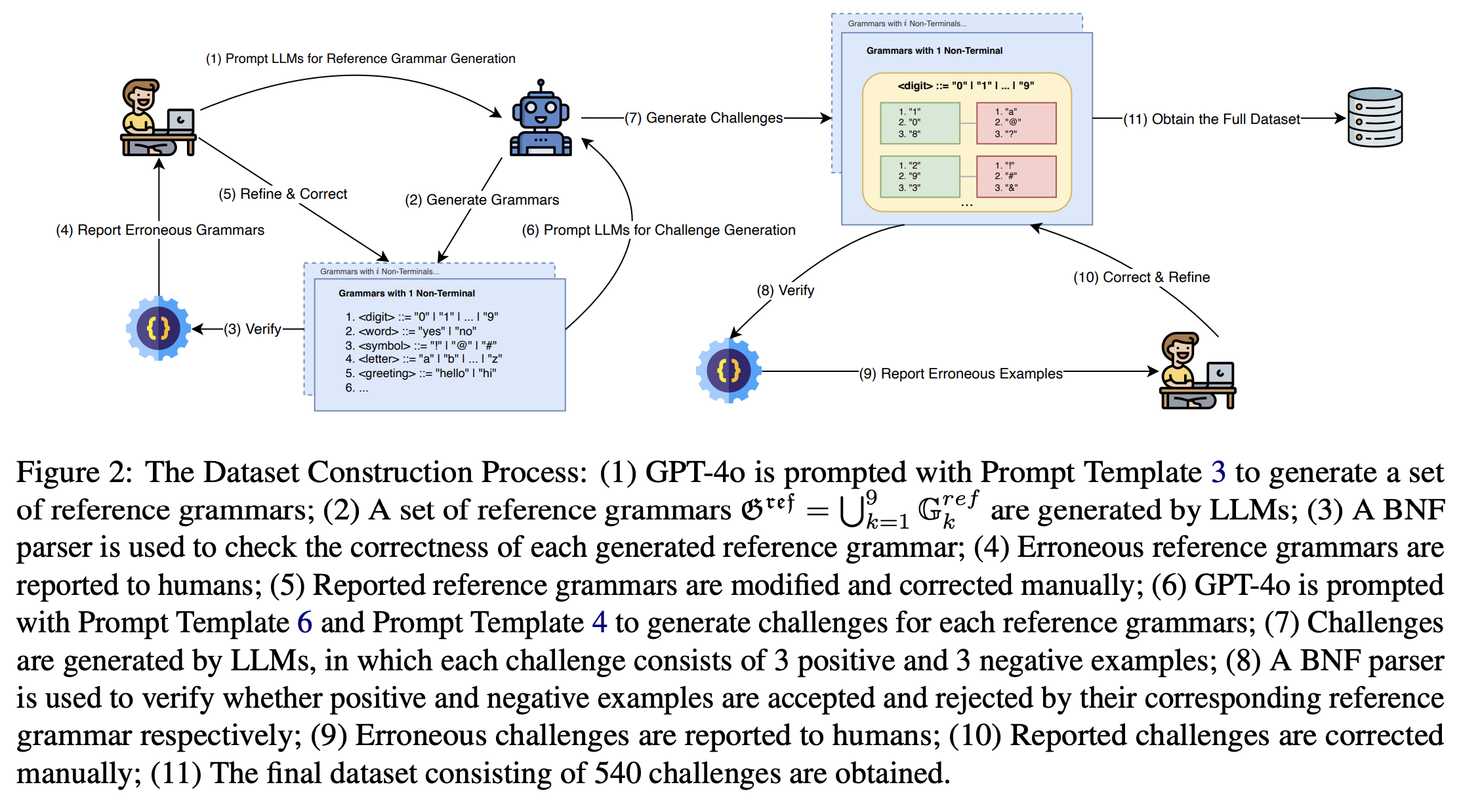

 Published May 2025
Published May 2025ToM-LM: Delegating Theory Of Mind Reasoning to External Symbolic Executors in Large Language Models
W Tang, V Belle
18th International Conference on Neural-Symbolic Learning and Reasoning
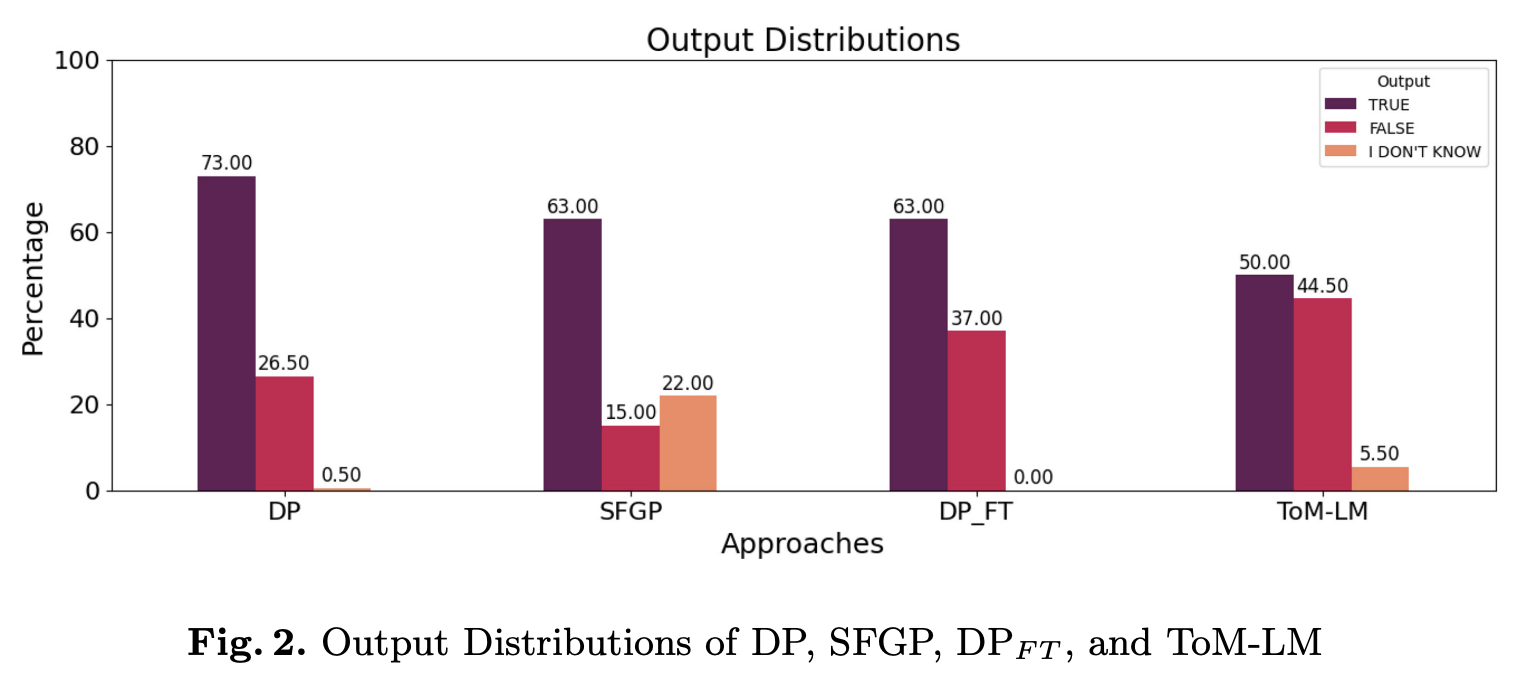
Theory of Mind (ToM) refers to the ability of individuals to attribute mental states to others. While Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown some promise with ToM ability, they still struggle with complex ToM reasoning. Our approach leverages an external symbolic executor, specifically the SMCDEL model checker, and fine-tuning to improve the ToM reasoning ability of LLMs. In our approach, an LLM is first fine-tuned through pairs of natural language and symbolic formulation representation of ToM problems and is then instructed to generate the symbolic formulation with a one-shot in-context example. The generated symbolic formulation is then executed by the SMCDEL model checker to perform transparent and verifiable ToM reasoning and give the final result. We demonstrate that our approach, ToM-LM, shows a significant improvement over all the constructed baselines. Our study proposes a novel view about externalizing a particular component of ToM reasoning, mainly reasoning about beliefs, and suggests generalizing it to other aspects of ToM reasoning.
 Published Apr 2024
Published Apr 2024





